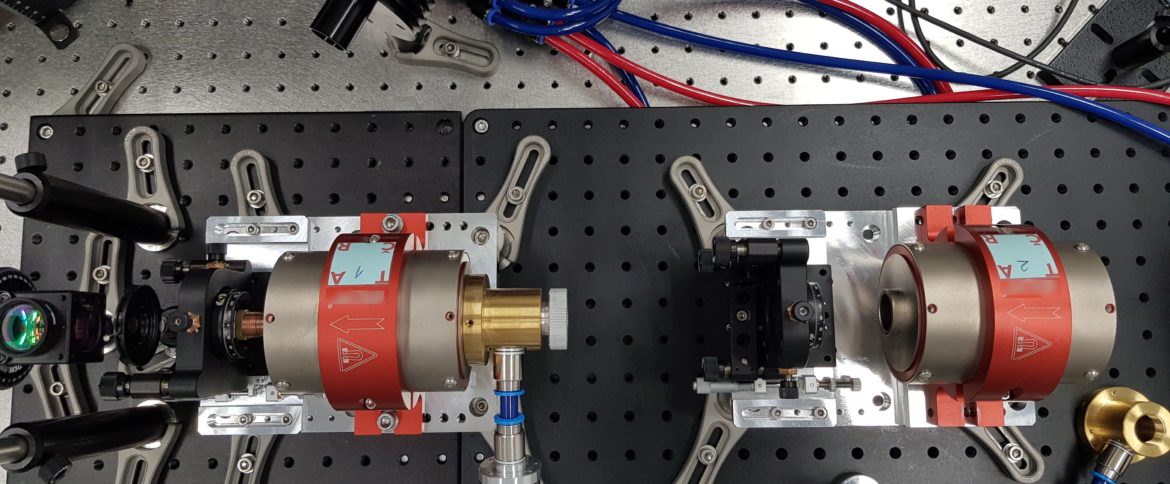
The HiLASE Centre Numerical Modelling team, led by Dr. Slezák, jointly with the team from the National Institute for Fusion Sciences (NIFS), Gifu, Japan has successfully characterised the magneto-optical properties of a Potassium Terbium Fluoride (KTF) crystal, manufactured by Northrop Grumman Synoptics, North Carolina, USA.
KTF is a key element for high-performance optical isolators, such as Faraday isolators, which are required by many industrial and scientific laser systems to achieve efficient optical separation between the user application and the high-power laser amplifiers, and to prevent dangerous light feedback into a laser cavity.
Initial experiments showed that KTF is an ideal candidate for the next generation of high-average-power Faraday isolators. Results were published in Optics Letters (vol 45, No.7, 1 April 2020, pp. 1683-1686).
With funding support from the Technology Agency of the Czech Republic (TA ČR), HiLASE Centre developed a high-performance functional sample of a 100W Faraday Isolator and is now looking for industrial partners interested to commercialise this high-average-power Faraday Isolator.
For more information, please contact solutions@hilase.cz.